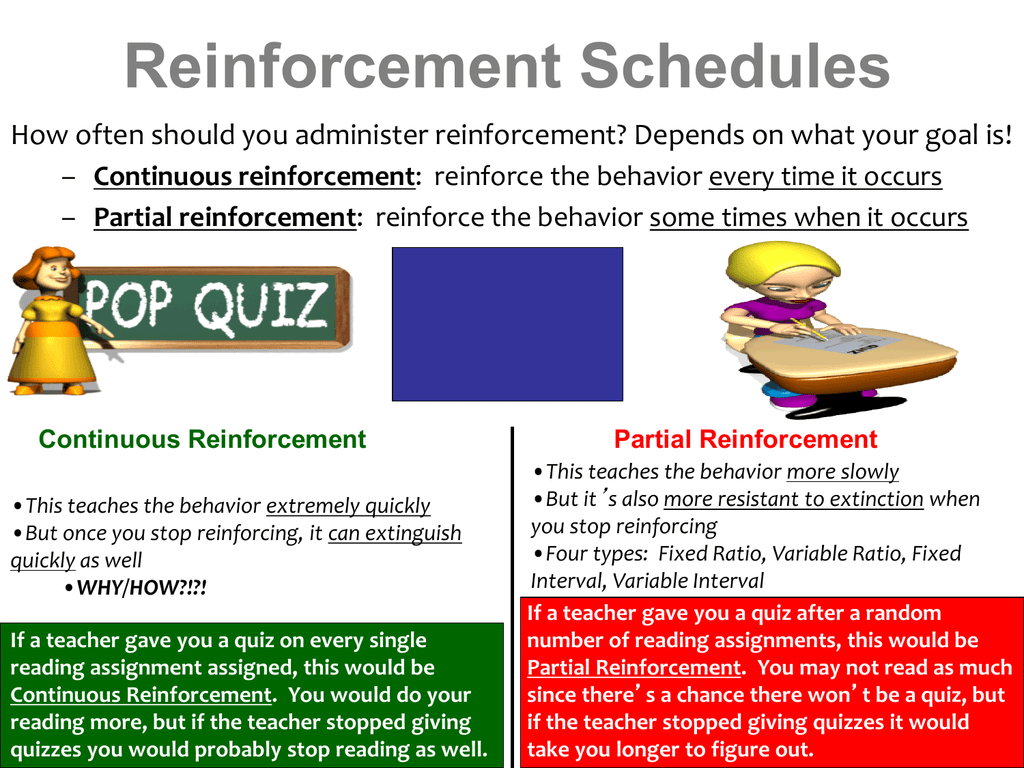
Maintains learned behavior longer than continuous R. Continuous reinforcement requires that you do it each time but partial reinforcement means you only reinforce part of the time.
 C Operant Conditioning Schedules Of Reinforcement Pv
C Operant Conditioning Schedules Of Reinforcement Pv
In general the partial reinforcement schedule is more effective for maintenance of behavior in the long term.

What is the difference between continuous reinforcement and partial reinforcement. Can be classified into four groups. Pigeon receives birdseed 12 sec. That is reinforcement is presented every time the animal performs the behaviour.
Only occasional reinforcement of a behavior resulting in slower extinction than if the behavior had been reinforced continually. This simply refers to the number of times that you reinforce a particular behavior. Fixed-ratio variable ratio fixed interval and variable interval.
Give an example of each and conclude by explaining which schedule of reinforcement is most effective. Effective when the behavior is new. Continuous reinforcement aExplain the difference between them.
When every desired behavior is reinforced. Also behaviors acquired from this form of scheduling have been found to be more resilient to extinction. Explain this phenomenon and what it shows about learning.
Continuous reinforcement is part of a reinforcement schedule. Explain the difference between continuous and partial reinforcement. Certain types of schedules may be more effective depending on the situation and the training purpose.
A schedule of continuous reinforcement CR involves 100 contingency between the behaviour and the reinforcement. Unpredictable amounts of time pass between completion of the behavior and the receipt of the reinforcement Variable-Interval Lab Ex human application and effectiveness Lab Ex. The continuous reinforcement plan is one method of reinforcement.
Abstract A continuous schedule of reinforcement CR in an operant conditioning procedure results in the acquisition of associative learning and the formation of long-term memory. A 50 partial reinforcement PR schedule does not result in learning. Click to read full detail here.
Reinforcing a behavior every time it occurs resulting in faster learning but faster extinction than only occasional reinforcement. A continuous schedule of reinforcement CR in an operant conditioning procedure results in the acquisition of associative learning and the formation of long-term memory. After completing trial 1 waits 19 sec.
Subsequently one may also ask what is continuous reinforcement. Distinguish between continuous and partial reinforcement Continuous reinforcement is when a behavior is reinforced every time it occurs Partial reinforcement is when a behavior is reinforced only some times. Partial reinforcement unlike continuous reinforcement is only reinforced at certain intervals or ratio of time instead of reinforcing the behavior every single time.
Explain the four schedules of reinforcement. Explain the four schedules of partial reinforcement fixed ratio fixed interval variable ratio variable interval and identify which schedule of reinforcement leads to the highest rates of. Fixed-interval fixed-ratio variable-interval and variable-ratio.
Partial reinforcement PR however refers to any schedule in which there is less than 100 contingency so that there are instances when the animals behaviour is not reinforced. Also behaviors acquired from this form of scheduling have been found to be more resilient to extinction. From the discussion the difference between these two types of reinforcement is inherently clear.
A 50 partial reinforcement PR schedule does not result in learning. There are two types of reinforcement schedules. The variable-ratio schedule is the most effective among the four types.
When some of the desired behavior is reinforced. A CRPR schedule results in a longer-lasting memory than a PRCR schedule. Partial reinforcement unlike continuous reinforcement is only reinforced at certain intervals or ratio of time instead of reinforcing the behavior every single time.
Halaman
Monash
Labels
-
If certain topics names or concepts appear more than once underline or highlight them and make sure they are prominent in your study guide....
-
The less-used punctuation symbols are virgule underline ellipsis points square brackets etc. The Well-Known Punctuation Errors to Know Befo...
-
Tuition runs 13770 for in state students and 13770 for out of state students. In a segregated post-Civil War country historically Black col...
-
Read all the questions BEFORE you read the passage. Diagnostics placement and demographic analysis. Compass Reading Test Success Compass ...
-
When a degree is considered terminal it means that it is the highest degree awarded in a given field. A degree that helps you to reach the ...
